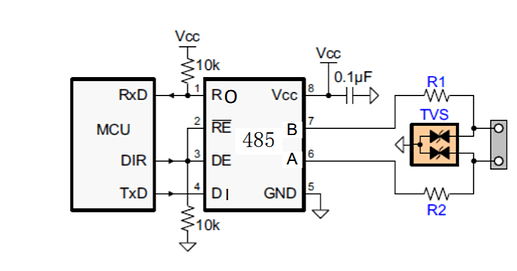
Seeed Studio RS-485 Breakout Board for XIAO and QT Py, with half-duplex tranceiver converting UART Serial to long-distance high-speed RS-485 transmission
Hi there,
"Man, these things are fantastic! Let me share why:
They’re built on proven technology with high-quality silicon that’s been refined over decades. Back in the day, Black Box sold loads of these as “Line Drivers,” which were considered cutting-edge when 9600 baud over 300 feet was the standard.
Fast forward to now, and the 12V DC version can transmit data over 5000 feet—far beyond its official 4000’ spec at 9600 baud! Pair it with EDDC (Extended Distance Data Cable), and you can push those limits even further at lower speeds.
Why are these units so impressive?
- ESD Protection: The driver outputs and receiver inputs boast ±12kV ESD protection to prevent latch-up. This level of protection is a game-changer for reliability and durability.
- Half-Duplex Communication: Like a single train track, only one direction is active at a time, but with the ability to reverse traffic flow when needed. Perfect for master-slave and multidrop network topologies.
From the Datasheet:
RS-485 and RS-422 are differential (balanced) data transmission standards designed for long-distance or noisy environments. RS-422 supports point-to-multipoint communication (1 driver and up to 10 receivers per bus). RS-485, on the other hand, is a true multipoint standard supporting up to 32 devices (drivers and receivers combined) per bus.
A few highlights of RS-485:
- Handles bus contention without damage.
- Extended Common Mode Range (CMR): +12V to -7V to manage ground potential differences and cable-induced voltages.
- Optimized for runs up to 4000 feet, with added resilience to external interference.
Where does the Xiao fit in?
The Xiao acts as the controller or “switcher,” managing protocol-specific communication. In a multidrop setup, it listens for its address or broadcast poll, receives data, and then toggles the line to transmit its payload over the wire pair.
For more details, check the Wiki—these are solid products if implemented correctly! ![]()
HTH
GL ![]() PJ
PJ ![]()
I was wondering what half duplex was… is sounds like full dupex would be better… but kinda like how people would rather have a 1/3 pound hamburger than a 1/2…
Hi there,
That would require 4 wires BTW, ![]() for full duplex or FDX…
for full duplex or FDX…
Half is HDX…
![]()
nice thnks for the info! I know just enough to be dangerious